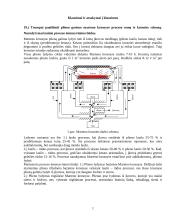
Konspektai
Material science - theory
1.Introduction. All engineers are involved with materials on daily basis. We manufacture and process materials, design and construct components or structures using materials, select materials, analyze failures of materials. As responsible engineers we are interested in improving the performance of the product we are designing or manufacturing. Civil and architectural engineers wish to construct strong, reliable, structures that are aesthetic and resistant to corrosion. Aerospace engineers demand lightweight materials that perform well both at high and low temperatures. Metallurgical, ceramic, and polymer engineers wish to produce and shape materials that are more economical and possess improved properties. 2.Types of materials. Materials are classified into several groups: metals, ceramics, polymers, semiconductors, composite materials. Materials in each of these groups often possess different structures and properties. Metals-are alloys which include steel, aluminium, magnesium, zinc, cast iron, titanium, cooper, nickel, and others. Metals are good electrical and thermal conductors, are high strength, stiffness, shock resistance. Combinations of pure metals are called alloys they are designed to improve properties or permit better combination of properties. Ceramics-brick, glass, refractory, abrasives, have low electrical and thermal conductivities are often used as isolators. Ceramics are strong and hard but very brittle. Are used in load bearing applications (impellers in turbine). Polymers include rubber, plastics and others adhesives. Produced by creating large molecular structures from organic molecules in a process known as polymerization. Have low electrical and thermal conductivities, low strength, not suitable for use at high temperatures. Thermoplastic polymers (long molecular chains aren’t rigidly connected) have good ductility and formability. Thermosetting polymers are stronger but more brittle, because molecular chains are tightly linked. Semiconductors silicon, germanium and a number of compounds such as GaAs are very brittle, they used at computer, electronic, communication applications. The electrical conductivity of these materials can be controlled. Used in transistors, diodes, processors, integrated circuits. Information is now being transmitted by light through fiber-optic systems; semiconductors, which convert electrical signals to light and vice versa, are essential components in these systems. Composite materials Composites are formed from two or more materials, producing properties that can’t be obtained by single material. Concrete, plywood and fibreglass are composite materials. With composites we can produce lightweight, strong, ductile, high temperature-resistant materials. 3.Structure-property-processing relationship. We are interested in producing a component that has a proper shape properties, permitting the component to perform its task for its expected lifetime. Properties of materials are considered in two categories mechanical and physical. Mechanical properties describe how a material responds to an applied force. The most common mechanical properties are strength, ductility and stiffness. Also how a material behaves when it exposed to a sudden, intense blow, continually cycled through an alternating force, exposed to high T, or subjected to abrasive conditions. How easy the material can be deformed into a useful shape. Physical properties, which include electrical, magnetic, optical, thermal, elastic and chemical behaviour depend on both structure and processing of a material. Structure of the material can be considered on several levels, all of which influence the final behaviour of the product. At he finest level is the structure of the individual atoms that compose the material. Electronic arrangement influences how the atoms are bonded to one another and helps determine the type of material-metal, ceramic, semiconductor or polymer. Metals, semiconductors and some polymers have a very regular atomic arrangement, or crystal structure. The crystal structure influences the mechanical properties of metals. Other ceramic materials and many polymers have no orderly atomic arrangement-they behave differently from crystalline materials. A grain structure is found in most metals, semiconductors, ceramics, polymers. In most materials more then one phase is present. Control of the type size distribution and amount of these phases within the main body of the material provides an additional way to control properties. Materials Processing produces the desired shape of a component from initial formless material. Metals can be processed by pouring liquid metal into mold (casting), joining individual pieces of metal , forming the solid metal into shapes using high pressures, compacting tiny metal powder particles into a solid mass, removing excess material. Ceramic materials can be formed into shapes by related processes (casting, forming, extrusion)Polymers are produced by injection of softened plastic into molds, drawing and forming. Materials can be treated at some T below its melting T to effect desire change in structure. 4.Environmental effects on material behaviour. Temperature changes in temperature dramatically alter the properties of materials. The strength of most materials decreases as T increases. Catastrophic changes may occur when heating above critical T. Very low T may cause a metal to fail in brittle manner even though the applied loads are low. High T can also change the structure of ceramics or cause polymers to melt or char. Corrosion. Most metals and polymers react with oxygen or other gases, particularly at elevated temperatures. Metals and ceramics may catastrophically disintegrate, polymers may become brittle. Materials are also attacked by a variety of corrosive liquids. A metal may be develop cracks or pits. Ceramics can be attacked by other liquid ceramics and solvents can dissolve polymers. Radiation. High energy radiation such as neutrons produced in nuclear reactors can effect the internal structure of all materials, producing a loss of strength, embitterment. External dimensions may also change. 5.The chemical bonding of atoms. There are many sub-atomic particles in the Universe. The main building blocks of all atoms are electron, proton and neutron. Proton and neutron are equal in mass when electron is only about one thousand of the mass of other two. electrical charges are carried by electrons. Relative massive protons and neutrons are concentrated in the core-or nucleus-of the atom, whilst the electrons are arranged in a series of orbits or shells around the nucleus. Each electron shell contains a specific number of electrons. The first shell contains 2 electrons and others have 8 electrons. Since the number of protons in the nucleus governs the total number of electrons, it follows that there are generally insufficient electrons to complete the final outer shell. Strong bonds are formed between atoms so that the atoms are let with completed outer electron shells. This is achieved by atoms either losing, gaining or shearing electrons. The electrovalent bond is the attractive force produced by reactions which take place between metals and non-metals. An atom of lithium contains only three protons in its nucleus and three electrons in orbit around that nucleus. Two electrons are in first shell and one is second. Atom of fluorine contains 9 protons and nine electrons 2 are in first shell and 7 in second. Since the nuclear charge of the lithium atom is relatively small its attraction for the lone electron in the outer orbit is weak and so, if a lithium atom and a fluorine atom is snatched away so that it joins the outer electron shell of the fluorine atom. This leaves the lithium particle with a complete first shell and complete second shell of fluorine particle. Lithium particle has positive charge and fluorine particle has negative charge. Charged particles are called ions. Metals always positive non-metals negative. These lithium and fluoride ions carry opposite charges they attract each other. Compound lithium fluoride forms a simple cubic type of crystal structure. The metallic bond. Most metals have up to 3 electrons in the outermost shell of the atom. These outer-shell electrons are loosely held to the atomic nucleus and as a metallic vapour condenses and subsequently solidifies these outer-shell electrons are surrendered to a sort of common pool and are virtually shared between all atoms in the solid metal. The metallic bond theory of metals explains many of the main characteristics of metallic elements: 1)all metals are good conductors of electricity. Current of electricity is in fact a stream of moving electrons. 2)Metals are good conductors of heat. The application of heat to a piece of metal causes electrons to vibrate more actively and these vibrations can be passed on quickly from one electron to another within the electron cloud. 3)Most metals are ductile because layers of ions can be made to slide over each other by the application of a shearing force. At the same time metals are strong because of the attractive force. 4)Metals are lustrous in appearance since the free, vibrating surface electrons fling back units of light as these fall upon the surface of the metal. The covalent bond is formed between atoms of non-metallic elements in which are strong attractive force between the nucleus and outer-shell electrons. Instead of a transfer of electrons from one atom to another there is a sharing of electrons between two atoms thus binding them together. Hydrogen atom has only one electron around a nucleus which has single proton. Two atoms of Hydrogen will combine a molecule of hydrogen and two electrons are sheared between two atoms completing the first electron shell for each atom. Similar is for carbon which has four electrons in its outer shell and it can combine with 4 atoms of hydrogen(methane gas). Unlike metals in which the outer-shell electrons can travel freely within the electron cloud so making metals conductors of electricity, the outer shell electrons in these covalent substances are securely held to the atoms to which they belong. These electrons are not free to move away and so the materials are excellent insulators since they can’t conduct electricity. 6.The crystal structure of metals and dendritic solidification. All metals and other elements can exist as either gases, liquids or solids. Gas is in vessel. When T increases the velocity and impacts between atoms increases and pressure with vessel increases. When T falls condensation occurs at the boiling point and in the resultant liquid metal the atoms are jumbled together and since they are held together only by weak force of attraction, the liquid lacks cohesion and will flow. When the metal solidifies the energy of each atom is reduced. The energy is given out as latent heat during the solidification process. After solidification each atom becomes firmly bonded to its neighbours by stronger forces of attraction, so the solid metal acquires strength. There are 3 different patterns in which the atoms of the more important metals arrange themselves on crystallization. Iron is a polymorphic element which exists in two principal crystalline forms. The body centred cubic form exists up to 910oC then it changes to a the face centred cubic form. When the T of molten pure metal falls to its freezing point crystallization will begin. The nucleus of each crystal will be a single unit of the appropriate crystal lattice. For example, in the case of a metal with a body centred cubic lattice, nine atoms will come together to form a single unit, and this will grow as further atoms join the lattice structure. These atoms will join the seed crystal so that it grows most quickly in those directions in which heat is flowing away most rapidly. Soon the tiny crystal will reach visible size, and form what is called a dendrite. Secondary and tertiary arms develops from the main backbone of the dendrite. The arms of dendrite continue to grow until they make contact with the outer arms of other dendrites growing in a similar manner near by. When the outward growth is thus restricted, the existing arms thicken until the spaces between them are filled, or until all the remaining liquid is used up. Impurities in cast metal. If the metal is pure then solidification is complete. If impurities were dissolved in the molten metal it would tend to remain in solution until solidification was almost complete. They would therefore remain concentrated in that metal which solidifies last. Concentration of segregation of impurities art crystal boundaries explain why a small amount of impurity can have such devastating effect on mechanical properties, making the cast metal brittle and likely to fail along the crystal boundaries. Influence of cooling rates on crystal size The rate at which a molten metal is cooling as it reaches freezing temperature affects the size of the crystals. A rapid fall in temperature however, will lead to some degree of undercooling due to this ultimate crystals will be tiny. When a large ingot solidifies the rate of cooling varies from outer skin to the core during the crystallization process. In the centre crystals are big in the outside crystals are small called columnar. Rapid solidification processing if cooling rates in the region will be 106 C/sec then non-crystal solid metals are obtained. 7. Polymorphism Many solid elements can exist in more than one different crystalline form and are said to be polymorphic. These difference forms are stable over different temperature ranges so that transition from one form to another takes place as the transition T is passed. Tin is also polymorphic existing as grey tin, ordinary white tin. WT the form with which we are generally familiar is stable over 130C while GT is table below 130C, but the change from one form to the other is very sluggish and WT will not normally change to the powdery grey from unless the T falls below 130C. Polymorphism is exhibited in a most spectacular way by the element carbon which can exist as diamond and as graphite. Under condition of extremely high T and pressure carbon atoms will link up with each other to form giant molecules in which the carbon atoms form a rigid crystalline structure showing the same tetrahedral pattern. Tetrahedral crystalline structure containing only carbon atoms is the substance diamond. Under a different set of condition of T and pressure carbon atoms will combine to form layer like molecules in another polymorph graphite. The layers are held together by weak Van der Wall’s forces generated by the spare electrons not used by the primary bonding system. These layers ill slide over each other quite easily so that graphite can be used as a lubricant. Carbon atoms in diamond are covalently bonded in such a manner that all valence bonds are used up no free electrons are present and so diamond doesn’t conduct electricity. In graphite however, spare electrons are present since not all of the valence electrons are used up in forming covalent bonds. Graphite is good conductor of electricity. 8.The tensile test. Tensile strength of material is the stress requires to cause fracture of a test-piece in tension. A TP of known cross-sectional area is gripped in the jaws of a testing machine and is subjected to a tensile force which is increased by suitable increment. When the TP begins to stretch rapidly the extensometer is removed-rapid extension is a sign that fracture is imminent and failure to remove the extensometer from the TP would probably lead to the destruction of the extensometer. The maximum force applied to the TP before fracture is measured. If the TP is stressed past the point of elastic limit, the material suddenly ‘gives’ that is suffers a sudden extension for very little increase in force this is called the yield point. Tensile strength=maximum force used/original area of cross-section. Tensile strength is a useful guide to the mechanical properties of a material. Force extension diagrams for heat-treated steels and for most other alloys don’t often show a well defined yield point. Hardness tests. Mob’s scale consists of a list of materials arranged in order of hardness, with diamond, the hardest of all at head of list and talc at the foot. The Brinell test. Best known of hardness tests. A hardened steel ball is forced into the surface of a TP by means of a suitable standard load. The diameter of the impression is then measured and the Brinell Hardness Number is found from H=(load/area of curved surface of the impression). In carrying out a Brinell test, certain conditions must be fulfilled. First the depth of impression must not be to great relative to the thickness of the TP. The width of the TP must be adequate to support the load. The Vickers pyramid hardness test. Uses a square based diamond pyramid as the indentor. One great advantage of this is that all impressions will be geometrically similar and accuracy of the result will not vary with depth of the impression. One more advantage of the Vickers hardness test is that hardness values for every hard materials are likely to be more accurate than the corresponding Brinell numbers. H=(load/surface area of indentation). The Rockwell test. It is particularly useful for rapid routine testing of finished material, since the hardness number is indicated directly on a dial, and no subsequent measurement of the diameter of the impression is involved. The depth of the impression is measured by the instrument and this is converted to hardness values. The TP which needs no preparation save the removal of dirt and scale from the surface is placed on the table of the instrument and the indentor is brought into contact with the surface under light load. This takes up the slack in the system and the scale is then adjust to zero. Full load is then applied and when it is subsequently release the TP remains under light load whilst the hardness index is read direct from scale. The scope scleroscope is a small portable instrument which can be used for testing the hardness of large components. The scleroscope embodies a small diamond tipped tup or hammer of mass ~25g which is released so that it falls from a standard height about 250mm inside a graduated glass tube placed on the test surface. The high of rebound is taken as the hardness index. 9.Impact test. These tests are used to indicate the toughness of a material and particularly its capacity for resisting mechanical shock. Brittleness resulting from a variety of causes. Is often not revealed during a tensile test. For example nickel-chromium constructional steels suffer from a defect known as temper brittleness this is caused by faulty heat-treatment, yet a tensile TP derived from satisfactorily treated material and one produced from similar material, but which had been incorrectly heat-treated might bought show approximately the same tensile strengths and elongations. In an impact test, how ever, the unsatisfactory material would prove to be extremely brittle as compare with the correctly treated one, which would be tough. The Izod impact test employs a standard notched TP which is clamped firmly in a vise. The Charpy impact test is of continental origin, and differs from the Izod test. In that the TP is supported at each end, whereas the Izod test uses a TP held cantilever fashion. Hounsfield balanced impact test makes use of a portable machine in which the striking energy is produced by means of two pendulums which move in opposite directions of each other. 10. The detection of surface cracks may be produced in a component as a result of heat-treatment or in a welded joint, by contraction during cooling. In some cases, such cracks may be discovered by careful visual inspection, with or without aid of a hand magnifier. The presence of very fine hair-line cracks, however, is less easy to detect, and some aid is generally necessary. 11. Wrought materials may contain slag inclusions and other flaws; whilst welded joints can suffer from any of these defects. Unfortunately, metal are opaque to light. Electromagnetic radiation will penetrate metals, and so enable us to ‘see’ into the interior of the material. X-rays and γ-rays are most widely used. X-ray methods. X-rays travel in straight line. The most efficient method of detecting faults in a body of metal is to take an X-ray photograph of its interior. Radiography of metals needs to be ‘harder’, that is of shorter wavelength, so that they will penetrate metal more effectively. These X-rays could damage our body tissues, so for this reason the equipment must be well shielded. A wall of ‘barium cement’ is often used. X-rays will penetrate region of casting containing the cavity much more easily, and so produce a denser image on the film. γ-rays methods They are harder than X-rays, and therefore able to penetrate a greater thickness of metal or a more denser metal. Exposure to γ-radiation is extremely dangerous. Originally, radium was used as a source of γ-rays, but artificially activated isotopes are now generally employed. One of the most useful activated isotopes is cobalt-60. Not only γ-rays harder, but, unlike x-rays, they cannot be switched off. A radioactive isotope emits from a few seconds to thousands of years. The technique used being similar to that used with x-rays. Ultrasonic testing is similar to yodel in the mountains and listen to a succession echo. In ultrasonic testing frequencies between 500 000 and 10 000 000 Hz are commonly used whereas our ears can detect sounds at frequencies only between 30 and 16 000 Hz. Figure: probe containing a quartz crystal, which transmit and receive high-frequency vibrations through the surface of material. Probe connected to amplifier, which converts and amplifies the signal. Vibrations will pas from the probe trough the metal and are reflected from the bottom inside surface back to the probe, which also acts as a receiver. Transmitted pulse and its echo are recorded. If any discontinuity is encountered, such as a blowhole, then the pulse is interrupted, and reflected back as indicated, because echo return in a shorter time, a ‘blip’ appears on the cathode-ray tube. The method is particularly suitable for detecting faults in sheet, plate and strip materials more than 6mm thick. 12. Eutectics Sometimes on solidification, the two metals cease to remain dissolved in one another, but separate instead, each to form its own individual crystals. Salt dissolved in water: when solution reaches its freezing-point, individual crystals of pure ice and pure salt are formed. Freezing-t. of salt is much lower than the pure water (ex. Salt on roads). This phenomenon is known as ‘depression of freezing point’, and it is observed in the case of many metallic alloys. Increasing amounts of the metal cadmium to the metal bismuth will cause its freezing point to be depressed proportionally; conversely, the addition of increasing amounts of bismuth to cadmium will have a similar effect on its melting-point. Composition 60%bismuth/40% cadmium is the eutectic mixture and the freezing and melting point at 140 C is called eutectic point. The metallic layers in the eutectic structure are extremely thin. When the material forming one type of layer is hard and strong and the other is soft and ductile, the alloy will be characterized by strength and toughness, since the strong through somewhat brittle layers are cushioned between soft but tough layers. Ex. Aluminum-silicon alloys. 13. Solid solutions Sometimes two metals which are completely soluble in each other in the liquid state remain dissolved in each other during and after solidification, forming what metallurgists call a ‘solid solution’. This is when two metals are similar in properties and have atoms approximately same size, these solutions are called ‘substitutional’. During solidification, one the metals will have melting point higher than the others and this metal will solidify at a faster rate. The core of a resultant dendrite contains rather more of metal with higher melting point, whilst the outer fingers of the crystals more of the metal with lower melting point. This effect called ‘coring’. The structure like a brick wall. Other type when atoms of one element smaller than the others and they fit between bigger into the interstices (spaces). This solution is called interstitial solid solution. Solid solutions are possibly the most useful of metallurgical structures, since they generally give a combination of strength, toughness and ductility. Intermetallic compounds Metallic oxides, sulphides, and chlorides are typical ionic compounds but sometimes two metals, when melted together, will combine to form a definite chemical compound called an intermetallic compound. It happens when two metals are unlike in their physical and chemical properties, and when one metal is strongly electropositive and the other is weakly electropositive. Intermetallic compound is always of fixed composition, in common with all chemical compounds, there is never any coring in crystals of such a substance in the cast state. Most compounds are hard and brittle, and are of limited use only in engineering alloys. 14. Equilibrium diagrams It a graphical method of illustrating the relationship between the composition, temperature, and structure, or state, of any alloy in series. These d’s are devised by experimental work and sometimes by guesswork. 15. Types of equilibrium diagrams There are a number of them, but we need to deal only with 3 of them, namely in which the characteristics of the diagram governed by the extent to which one metal forms a solid solution with the other. The possibilities are that: 1. two metals are completely soluble in each other in all proportions in all in the solid state, 2. two metals are completely insoluble in each other in the solid state, 3. two metals are partially soluble in each other in the solid state. An alloy sys in which 2 metals are soluble in each other in all proportions in both liquid and solid states: An example of this type is nickel-copper alloy. Atoms of nickel and copper are almost same size, both crystallize in similar face-centered cubic patterns and they form mixed crystals of a substitutional solid-solution type when a liquid solution of the metals solidifies. The eq.d. will have been derived from a series of cooling curves, except that a pyrometer capable of withstanding high temperatures would be required for temperature measurements. An alloy sys in which 2 metals are soluble in each other in all proportions in the liquid state, but insoluble in solid state: 2 metals form homogenous liquid when melted together, but on solidification they separate and form individual crystals of the 2 pure metals (Cadmium and bismuth). An alloy sys in which 2 metals are soluble in each other in all proportions in the liquid state, but partialy in solid state: this case is intermediate case between previous 2, since it represents a compromise between the extremes of complete solid solubility on the one hand and insolubility in the solid state on the other. 16. Steel-making Until Henry Beassemer introduced his process for the mass-production of steel, in 1856, all steel was made from wrought iron. Nowadays wrought iron is no longer produced, only in very small quantities for special purposes. Bessemer process is obsolete. In Britain the bulk steel is made by one of the basic-oxygen processes developed since 1952, or in the electric arc furnace. Basic oxygen steel-making. It’s involving oxidation of impurities present in the original charge, so they form slag which floats on the surface of the molten steel. Electric-arc steelmaking is the only alternative process in Britain to BOS, to which it is complementary rather than competitive. Electric-arc furnaces used for the treatment of ‘hot metal’ and of process scrap as well scrap from other sources. The high cost is largely offset by the fact that cheap scrap can be processed economically to produce high-quality steel. Cast iron-making Ordinary cast iron is the similar in composition to the crude pig iron produced by the blast-furnace. Features that makes cast iron important material: 1)It is cheap metallurgical substance, since it is produced by simple adjustments to the compositions of ordinary pig irons. 2)Mechanical rigidity and strength under compression are good. 3)It machines with ease when a suitable composition is selected. 4)Good fluidity in the molten state leads to the production of good casting-impressions. 5)High-duty cast irons can be produced by further treatment of irons of suitable compositions. 18. Classification of steels Steels are alloys, which ingredients are: a) iron, b)carbon in quantity not exceeding 2%. High alloy complex products composed of iron, chromium, nickel and so on. Steels are also classified in two groups: 1) structural steel and 2) tool steel. Groups by combining classifications: 1)carbon structural steel. 2)carbon tools steel. 3) alloyed structural steel. 4) alloyed tool steel. 5)highly alloyed structural steels with special physical and physico-chemical properties. Groups classified according their quality characteristics: 1)ordinary quality steels. 2)higher quality steels. 3)quality steels. 4)high-quality steels Carbon steels are divided into 3 groups according to quality: ordinary quality, higher quality and quality steels. Ordinary and higher q steels are indicated in State standards, according to these all structural carbon steels are divided into three groups: a)steels with guaranteed mechanical properties; their chemical composition is optional b)steels with guaranteed chemical properties; c)steels with guaranteed compositions and mechanical properties; Quality structural carbon steels are characterized according to quality specifications as follows: 1)the mechanical properties of these steels are somewhat higher than those ordinary steels. 2)specified either by chemical composition or by mechanical properties 19.The composition of cast iron Ordinary cast iron contains: Carbon 3-4%; Silicon 1-3%; Manganese 0.5-1%; Sulphur0.1%; Phosphorus 1%. Carbon may be present in the structure either as flakes of graphite or as a network of hard, brittle iron carbide. Silicon to some extent governs the form in which carbon is present in cast iron. It causes cementite to be unstable, so that it decompresses, thus realizing free graphite. Therefore a high-silicon iron tends to be a grey iron, whilst a low-silicon iron tends to be a white iron. Sulphur has an opposite effect on the structure-it tends to stabilize cementite, and helps to produce white iron. Sulphur causes excessive brittleness in cast iron. During the melting of cast iron in a cupola, some silicon is inevitably burned away, whilst some sulphure is will be absorbed from the coke. Manganese toughens and strengthens an iron, partially because it neutralizes much of the unwelcome sulphur by forming a slag with it, and partly because some of the manganese dissolves in the ferrite. Phosphorus forms a very brittle compound with of the iron. Like silicon it increases fluidity and considerably improves the casting qualities of irons which are to be cast in thin sections. Thus cast-iron water pipes contains up to 0.8% phosphorus, whilst many of the old ornamental castings obtained up to 1% of the element. 20. The Influence Of Cooling Rate On The Properties of a Cast Iron. When the precence of silicon in an iron tends to make cementite unstable, the latter does not break up to decomposite instantaneously:this process of decomposition requires time.If such iron solidifies rapidly,the carbon may well be ‘tapped’ in the form of hard cementite, and so give rise to a white iron. If this will solidify very slowly, the cementite has more opportunity to decompose, forming graphite, and so produce a grey iron.This effect can be showed by casting a ‘wedge-bar’ in an iron of suitable composition.If this bar is fractured, and hardness determinations are made at intervals along the centre line of the section, it will be found that the thin end of the wedge has cooled so quickly that decomposition of the cementite has not been possible. This is indicated by the white fracture and the high hardness in that region. The thick end of the wedge,however,has cooled slowly,and is graphitic,because cementite has had more opportunity to break up. Here structure is softer. Such casting has a hard surface skin. It consist of cementite which has been prevented from decomposing by the chilling action of the mould.Iron beneath the surface has cooled more slowly,so that cementite has decomposed,released graphite. Cast iron sould be presented in the form of small flakes of graphite. It depends on:the silicon-content of the iron, and the rate at which the iron solidificies and cools. When casting thin sections,iron shoul be coarser grey frcture(higher silicon content).An engineering cast iron contains some cementite,if such an iron is heated in 700C it forms to graphite & iron.The volume increases and occurs cracks on the surface.Hot gasses penetrate cracks and surface disintegrates.To prevent growth in cast irons,it sould has no cementite. 21.ORDINARY CAST IRONS. HIGH DUTY CAST IRONS. MALLEABLE CATS IRONS. ALLOY CAST IRONS. Ordinary cast irons fall into 2 main groups:engineering irons,they must posses reasonable strength & toughness & good mashinability. Cast iron must contain silicon in accordance with the cross sectional thickness of the casting.It may be >25% for thin castings, but 13% of cromium.these steels are used in domestic kitches, refrigerator parts, table ware. Second type of stainless steel is used for ornamental and constructional works. Much of it is used in chemical plant. Austenitic stainless steels are hardened by quenching from 1050C. because of precipitation of chromium carbide, these steels are unstable for welding. The temper applied for welding 650-800is enough for chromium carbide to precipitate there,and corrosion will occur. 25.SINTERED TOOL MATERIALS, are not steels,but their properties is similar to high speed steels. They contains particles of a hard constituent in a hard, tough matrix. Sintered carbides are based on tungsten carbide and cobalt. They are relatively brittle. Aluminum oxide is one of the hardest metallic oxides available. It can be used as cutting tool material. They have low friction properties, high resistance to abrasion and chemical attack. HEAT RESISTING STEELS.the main requirements of steel to be used at high temper.are: resistance to oxidation and strength. Resistance of oxidation is effected by adding chromium, it protects the material from futher attack. To increase strength is added tungsten, titanium.MAGNETIC ALLOYS. Magnetic fields are generated by the spin of electrons within the orbits of atoms. But there is very weak magnetic properties because electrons are in pairs, only iron-along with nickel,cobalt,etc. are magnetic. The process of magnetization aligns atoms in one direction. Magnetically soft materials displaying high magnetic permeability. These materials are used in transformer cores,communications engineering. Magnetically hard materials,posses very high remanence and coercive force. Sintered alloys are used in loudspeakers, computer devices. 26.ALLOY STEEL & TEIR CHARACTERISTICS (RUSSIAN STANDART). Grades of alloy steels are designated by two digit numbers indicating the carbon content, and by letters indicating the alloying elements. E.g. X-chromium, H-nickel… Grades for alloy and high alloy structural steels are the same. They are designated by one digit numbers,indicating carbon content and one or more letters for the elements contained. Grades for electrical purposes are designated by letter Э and two digits.the first no. indicates silicon content,the designation of guaranteed magnetic properties. For springs are used steels which contain 0.60-0.90 % of carbon. High speed steels should have high mechanical strength at elevated temperatures. Such steels retain their hardness at 600C. they are alloyed with tungsten, chromium and vanadium. The Russia Standart specifies 2 grades: P18 & P9.No indicates % of tungsten. Stainless steels posseses high resistance to corrosion. All types of such steel are alloyed with cromium. It is used in steam turbine blades, household articles… acid resisting steels are resistive to corrosion by attacks by acids and chemicals. It is alloyed like stainless steel,but there is added titanium, niobium,manganese. There is also non-magnet, high ohmic resistance, non-scaling,wear resistance and electrical steels. Electrical steels are dynamic & transformer irons. These steels are alloyed with silicon. Electrical steels have high magnetic induction, low coersive force and low watt losses. Russia Standart specifies 5 gardes of steel for permanent magnet. 27.NORMALISING. the main purpose is to obtain a structure which is uniform throughout the work-peace,and is free from loced-up stress. E.g. forging may lack in structure,because outer layers received more deformation than the core. Thicker sections which received little working will be coarse grained, and vise versa. Normalizing involves heating a piece of steel to just above its critical temperature. When the work piece reaches lower critical temp., the pearlitic part changes to austenite. When the work piece is withdrawn from the furnace,the austenite changes back to structure of ferrite and pearlite. The grain size may be alittle smaller,than that in heavy sections, because of fast rate of cooling. 28.ANNEALING. it is a number of different heat treatment processes,which are applied to different steels. Sand castings contain a little carbon,so structure consisting ferrite & pearlite is obtained. If it will cool slowly,its grain size will be coarse, and it will suffer from brittleness. Annealing process: the casting is heated to its critical temperature,so that coarse grained structure will be changed by fine grained austenite. It is held for some time in such temperature, then it is cooled and in structure rises fine grained ferrite & pearite. Cooling with a furnace protects material form cracks & distortion. Spheroidisation annealing is applied to high carbon steels in order to improve machinability. This process is carried out below the critical temperature,so no phase change is involved. Annealing of cold-worked steel causes recrystalisation of the distorted ferrite,so producing new ferrite crystals,which can be recold-worked. Such materials must be heated to a temperature above the min which will cause recrystallization. 29.PRINCIPLES OF HARDENNING. If a steel containing carbon is heated until its structure is austenitic and cooled quickly it becimes much harder,than it would be cooled slowly. Austenite which is above its critical temperature ia a soft, malleable material, that is why it is shaped by hot working process. When we quench austenite a very hard, brittle structure is produced. Under a microscope it looks like needle shaped crystals, cooled martensite. Fast cooling prevent formation of pearlite. If it is cooled not so fast,between martensite occurs dark patches, and metal isn’t so strong. To determen the relationship between cooling rate of a steel and its final microstructure is used TTT curves.(time-temperature-transformation). A TTT diagram consist of 2 C-shaped curves.The left indicates time interval before carbon steel begins to transform, right shows the time which must elapse before transformation is complete. 2 parralel lines near the foot of diagram shows where martensite begins nad finishes transformation. Sharp variations in cross section,and presence of cracking, groves are increasing the possibility of quench-cracking,by causing uneven rates of cooling. Process of hardening: to harden eutectoidical steel, it must be heated above its critical temperature,and the quench in some medium to cool by required rate. 31.Solid, liquid and gaseous hardening. Hardening process makes use of the fact that carbon will dissolve in appreciable amounts in sold iron. The carbon atoms are small enough to infiltrate between the lager iron atoms, to do so steel must be carburised at the temperature above the upper critical temperature (9000-9500). Carburising-material heating above their upper critical temperature for a long enough to produce a carbon-rich surface layer of sufficient depth. Carburising in solid media. Most familiar process. Components to be treated are packed into steel boxes, along with the carburizing-material, so that space 50 mm exists between them, closed and slowly heated (900-9500) according to the depth case required, after heating it’s slowly cooled in the boxes. Mixtures such as charcoal or charred leather along an energizer (mixture of sodium and barium carbonate) may account for about 40% of total. Carburising in liquid media. Carried out in baths of molten salt witch contain 20 to 50% sodium cyanide, together with as much as 40% sodium carbonate, and varying quantities of sodium or barium chloride. Mixture is heated in iron pots to a temperature of 870-950 and the work is immersed about five minutes upwards, according depth is required. The main advantages of cyanide are: 1.the temperature of a liquid salt bath is uniform throughout, can be controlled accurately by pyrometers. 2. the basket of work can be quenched direct from bath. 3. the surface of the work remains clean. Carburising in gaseous media. Materials are heated at bout 900C in atmosphere containing gases witch will deposit carbon atoms at the surface of the components. Gases-hydrocarbons methane and propane. Main advantages of the process: 1.the surface are clean after treatment.2. the necessary plant is more compact for a given output. 32.Heat-treatment after carburizing. Heat-treatment consists of two main parts: 1. Refining the core. The component is first heat-treated to refine the grain of the core abou (723C), and so toughen it. This is done by heating the component to a temperature just above the upper critical temperature for the core, so that coarse ferrite/pearlite will be replaced by fine-grained austenite. The component is then generally water-quenched, so that a mixture of fine-grained austenite. 2. Refining the case. The component is heated so that the structure of the case changes to fine-grained austenite about (760C). Quenching then gives a hard case of fine-grained martensite. At the same time, any brittle martensite preset in the core as result of the first quenching process will be tempered to some extent by the second heating-operation. Finally, the component is tempered at about 200C, to relieve any quenching-stresses present in the case. Alternatively, the work may be cooled slowly from the carburising temperature, to give maximum ductility to the core. It is then reheated to 760C, and water-quenched. This treatment leaves the core quite soft, but hardens the case, witch will be fine-grained, due to the low quenching temperature. 33.Nitriding. Carbonitring. Ionitriding. Nitriding. The work contained 500C for between forty and one hundred hours, according the depth of case required. The treatment takes place in a gas-tight chamber through which ammonia gas is allowed to circulation. Some of the ammonia decomposes, releasing single nitrogen atoms, which are at once absorbed by the surface of the steel. Carbonitring. Is a surface-hardening process which makes use of a mixture of hydrocarbons and ammonia. It is therefore gas treatment-a mixed carbide-nitride case is produce. Carbonitring is an ideal process for hardening small components where great resistance to wear is necessary. Ionitring. The work load is made the cathode in a sealed chamber containing nitrogen under near-vacuum conditions. Under a potential difference approaching 1000volts the low-pressure nitrogen ionizes. In a great velocity and temperature (400C-600C) nitrogen atoms penetrate the surface. 34.Flame-hardening. Induction-hardening.Flame-hardening The surface is heated to a temperature above its upper critical temperature and is immediately quenched by a jet of water issuing from a supply built into the torch-assembly. Symmetrical components are conveniently treaded in this process, the whole circumference being treaded simultaneously. Only steels with 0.4% carbon can be hardening sufficiently in this way. Before being hardened, components are being normalized and tough ferrite-pearlite core. Induction-hardening is heated simultaneously by means oh an induction-coil. This coil carries a high-frequency current, which produces eddy currents in the surface of the component, thus rising its temperature. Typical frequencies used are: 3000hz – depth 3-6 mm, 9600hz-depth 2-3 mm. This process lends itself to mechanization; so that selected regions of a symmetrical component can be hardened, others left soft. 35.Quality control of heat treated articles and tools (finished products). Control of the final quality characteristics of heat-treated articles and tool is the main and most important kind of control of quality of the finished product. The quality control applied to the fully heat-treaded articles and tools aims to determine whether they conform to establish specification and standards. Therefore this kind of control is considered as the final and most responsible produce in production control. Specifications are developed on the basis of the following sources: 1.standards, for typical articles and tools; 2.plant technical requirements; 3.drawings. According to the technical requirements formulated in the standards, specifications and drawings , the articles and tools are to be tested for: 1.hardness; testing for hardness is the most commonly used kind of inspection; 2.mechanical properties; 3.physical properties; 4.depth of a case, for articles witch have been case-hardened. 36.Melting furnaces. There are several types of furnaces used for the melting of metals and these furnaces may be heated by solid, liquid, or gaseous fuels, or by electrical power. Cupola, the fuel used is coke and there will be some pick-up of carbon by the metal. Reverberatory, furnaces may be fired by solid, liquid or gaseous fuels. Products of fuel combustion are allowed to come into act with metals. They design very different according to the fuel, but very spread used in melting of different metals and alloys. Electrical furnaces: 1.crucible: operates on the induction principle, this system of melting is widely used for the production of high-quality metals and alloys. Arc: are used extensively in the production of alloy steels. The arc is struck between the carbon electrodes and the metal. 37.Sand casting. It’s most common casting. Liquid metals is poured into a shaped cavity moulded in a sand. Moulding sands have fairly low thermal conductivity so that the rate of solidification of liquid metal within a sand mould is fairly slow, giving rise to a coarse crystal grain. Stages in making a small sand mould: 1.Bottom half of pattern is placed on mould board in bottom half of flask. 2.now it filled with sand, ramed. 3.the bottom rolled over, the top half of pattern and flask is placed in position. 4.the top half is prepared in the same way. 5.the flask is separated, the patterns are moved, the core is set in place the flask closed. 6.when the flask is closed and clamed together it is ready for pouring of metal. 38. Die casting. Investment casting. Centrifugal casting. Gravity die is very similar in principle to sand casting, in that die design must include riser heads to feed solidification shrinkage.the dies moulds made of steel. The main advantages of the process are that a more rapid solidification rate produces a finer crystal grain structure than in a sand casting. In consequence the die casting will possess a higher strength, better dimensional control and surface finish. There are two types of process 1.hot chamber die, liquid metal enters the goose-neck and is forced into the die attached to the furnace by either a mechanical piston or pneumatic pressure giving injection pressure up to 40 MPa. In 2.cold chamber process, the charge of liquid metal is poured into a transfer chamber from a holding furnace immediately prior to injection, pressure 150 MPa, into the die. Investment casting. Used for making components that have withstand very high temperatures and stresses in service. They have high standards and accuracy. In process, a master mould is produce in a readily machineable alloy and mould is used for the production of accurate patterns in wax or a low melting alloy. Centrifugal casting. A cylindrical mould shell, lined with moulding sand, is rapidly rotated about its longitudinal axis and liquid metal is poured in. Properties very good and rotation action ensure that metals will be without slags. 39. Hot working. refers to a plastic deformation carried out at temperatures in excess of the recrystallisacion temperature of the metal. Hot working processes are rolling, forging and extrusion. In rolling operations the ingot is passed between two large cylindrical rollers and the roll surfaces have to be providing with flood cooling to prevent overheating of the rolls and possible welding between ingot and rolls. Fluids are used depending on a nature of the material being rolled. Forging means the shaping of metal by hammer (accelerated by gravity or by gravity and steam pressure) blows or by slow application of pressure. Forging operations may be carried out using either forging hammers or forging presses. Pressure is slowly applied and plastic deformation tends to occur fairly uniformly throughout the material. Hot Extrusion process. The hot ingot is forced by to flow, under pressure, through a shaped shell, or die, in a same way to the flow of tooth paste from a collapsible tube. It is possible to extrude almost infinity variety of sectional shape. Direct extrusion. Pre-heated ingot is placed in the chamber of the press and the force applied by a piston, through a pressure pad, causing the ingot to flow plastically and extrude through the die aperture. In indirect extrusion – no relative movement between the billet and container. Die is attached to a hollow ram and is forced into the billet. The extrusion flow is trough the die and hollow ram in a reverse direction to the ram movement. 40. Cold working. It is plastic deformation performed at temperatures below the recrystalisation temperature of metals. Crystal structure becomes broken up and distorted and the material becomes strain or work hardened. The mechanical strength is increased by it and materials become harder, but more brittle. The electrical resistivity is also increase. Eventually, metals becomes so hard that further cold working would cause fractures. Material may be softening by heating it to temperature above the recrystallisation temperature allowing grains to recrystallise. Advantages: very good dimension control, good surface finishes can be achieved. Cold rolling is used for the production of sheet and strip material. Sheet and strip metal may be formed into an infinite variety of shapes. Roll forming, deep drawing, pressing, rubber forming, stretch forming, and spinning are some of the processes that can be used for the production of complex and hollow shapes from sheet and strip material. 41.The cutting process Metal cutting is a cold working process in which a cutting tool forms chips. The cutting tool. presents a wedge-shaped point to the work in ideal orthogonal cutting, the cutting edge of the tool is normal to the direction of motion. There is severe deformation by shear in a plane, the shear plane, resulting in the formation of a chip. Considerable compression Occurs in the deformed material and the thickness of the deformed chip produced will be greater than the depth of cut. There are two aspects of the tool geometry which are of importance, these are the rake angle and the clearance angle. The rake angle of the cutting face, which is measured from the normal to the workpiece surface, influences the shear angle and the amount of chip compression. The clearance angle is necessary to reduce friction between the tool and the machined surface. The geometry of a single point cutting tool has a major influence in determining the efficiency of a cutting operation. Increasing the rake angle has the effect of reducing both tool forces and friction and giving a less deformed and cooler chip. However, the provision of a large rake angle gives a smaller tool section, thus reducing the strength of the tool. The most effective rake angle for any cutting operation will be determined by the nature of both the workpiece and cutting tool material. Chip formation The type of chip formed in cutting processes may be continuous or discontinuous. Soft; ductile materials will deform plastically to a very large extent and a continuous chip will be formed. With a less ductile metal, severe work hardening of the cut material will lead to a series of fracture and give rise to a discontinuous chip. Under some conditions, a built-up edge will form. This is the adherence of material to the cutting tool face and it alters the geometry of the tool, effectively increasing the rake angle and reducing the cutting force. When cutting at relatively low speeds using a cutting fluid, a smooth machined surface is formed and the chip surface is also smooth and slides across the rake face of the tool. As the cutting speed is increased, there is an increase in the temperature of both chip and tool face and, above a certain critical value of cutting speed, there will be some welding of chip material t6 the tool, the built-up edge, altering the tool cutting profile. 42.Cutting tool materials The properties required in a cutting tool material are high hardness, the ability to retain hardness at elevated temperatures and to possess a degree of toughness sufficient to minimize the incidence of chipping and cracking. The main categories of cutting tool materials in use are: Carbon tool steels Carbon tool steels contain between 0.6 and 1.5 per cent carbon and are used in the hardened and tempered condition. They lose much of their hardness, through Tempering when heated above 300"C. High speed steels These are highly alloyed steels containing tungsten, chromium, vanadium and molybdenum, the most widely used composition being 18 per cent tungsten, 4 per cent chromium, 1 per cent vanadium and 1 per cent carbon. These steels retain their hardness at reasonably high temperatures and do not soften appreciably until they are heated above 600°C. Cemented carbides Cemented carbides, also known as cermets and hard metal, are composed of carbides of tungsten, titanium, niobium and other metals, in a matrix of cobalt and are made by Powder metallurgy processing involving compaction and sintering. Coated carbides These are cemented carbides provided with a thin coating, typically about 5um thick, of a harder ceramic material. The coating may be applied by chemical vapour deposition (CVD) or by sputtering. Titanium carbide, titanium nitride and alumina are among the hard coatings used and in some cases a multi-layer coating may be applied Ceramic tools A number of ceramic materials are used as disposable tool tips. These include alumina Cubic boron nitride and polycrystalline diamond (PCD). These ceramics are harder than cemented carbides but are of lesser toughness. They are capable of cutting very hard materials such as superalloys, and of operating at much higher cutting speeds than is possible with cemented carbides, PCD, interacts with iron at high temperatures and is not suitable for cutting steels. 43. Machinability Machinability is the relative ease with which a material may be machined by a cutting process. A very soft and ductile metal may spread under the tool cutting pressure, with the result that the tool tends to become buried in the workpiece and a tearing, rather than a clean cutting action, may occur. A similar effect can occur with soft thermoplastics. In the case of a less ductile metal, the severe work hardening effect will lead to the creation of a series of fractures giving discontinuous chip formation. It is this type of chip formation which is desirable for high-speed machining with automatic machine tools. For the best machining characteristics, the requirements are for low hardness, coupled with low ductility. The Machinability of a metal can be improved by any means that will decrease the ductility and increase the susceptibility to fracture. This includes work hardening and alloying to give solution or dispersion strengthened materials- Of course, the material must not be made too hard, as then it will increase the difficulties of cutting and lead to very rapid tool wear. Multiphase alloys often machine well because the additional phases provide discontinuities within the microstructure and assist in the formation of discontinuous chips. The machining characteristic of some common materials: Alloy steels, Cast irons, Aluminium and its alloys, Copper and its alloys, Magnesium and its alloys, Plastics materials, Ceramics. 44.Single point machining The main machining processes involving use of a single point tool are shaping and planning, which generate flat surfaces, and turning on a lathe to generate curved surfaces, although other operations such as boring and facing can also be carried out on a lathe. Shaping and planning Both shaping and planing are machining processes for producing fiat surfaces by the straight line cutting action of a single point tool. Most shaping is in the horizontal plane with a horizontal push-cut, the cutting t061 being pushed across the work by a ram.. During the return stroke of the ram. Turning, boring and facing Turning is a rotational cutting process in which the work rotates and tool feed is parallel to the axis of rotation. Turning is only one of several cutting operations which may be made on a lathe Lathes Centre lathes are probably the most widely used types of machine tools. There are many different types and sizes of lathe but basically a lathe provides a rotary motion to the work. Multi-point machining In multi-point machining, two or more cutting edges of the same tool are in operation at the same time. The main multipoint machining processes are drilling, milling, broaching and sawing. Drilling The provision of cylindrical holes in components is a major requirement and the majority of machined holes are produced by drilling. The most common type of drill in use today is the twist drill. Milling Milling is a metal cutting process in which a multi-point tool rotates and the work feeds past the tool. computer numerical control (CNC) machining For modem day mass production, machine tools are computer controlled and numerical control The milling machine is controlled by a dedicated mini or microcomputer attached or assigned to it. Broaching This is a metal cutting operation in which a tapered multi-toothed tool, a broach; is pushed or pulled through (internal broaching) or over (external broaching) 45.Abrasive machining and finishing Abrasives are very hard materials and they are used for the removal of material by scratching, grinding or polishing. The abrasive machining processes enable components to be produced to close dimensional tolerances and with good surface finishes. Until the development of some of the non-traditional machining techniques, the only methods available for the machining of extremely hard metals and ceramics were abrasive processes. Abrasives Many different materials are used as abrasives, the common feature being that they are all of high hardness. The materials used include silica, alumina, silicon carbide, cubic boron nitride and diamond. Abrasive powders may be consolidated and bonded into a solid shape, such as a grinding wheel, made into coated abrasives, that is, bonded to a flexible paper or cloth backing, or used as a paste or powder within a carrying fluid. The abrasive powders are sized and graded to produce a wide range of wheels, papers and pastes. Grinding This is material removal by abrasion and may be effected by using a grinding wheel or a coated abrasive. Each abrasive particle acts as a mini-single point cutting tool, producing very small chips. Grinding wheels There are many different types of grinding wheel available as there are many variable parameters, including type of abrasive, grain size and packing density of abrasive, type of bonding and amount of bonding material. Abrasive jet machining This is a process which is used for cutting holes or slots in very hard materials by means of a jet of high pressure air or carbon dioxide carrying entrained dry abrasive particles. Ultrasonic machining This is an abrasive machining process using an abrasive slurry in connection with a form tool. The form tool holder is vibrated by a piezoelectric transducer at a frequency of about 20 kHz and the tool is fed slowly into the work. The abrasive particles at the tool/workpiece interface are accelerated by the vibrating tool and perform the cutting. This process is suitable for machining holes, slots and shaped cavities in hard metals, ceramics and composite materials. Barrelling This is a. general term covering several abrasive cleaning and finishing processes. In barrel cleaning, or tumbling, components are loaded into a cylindrical drum together with an abrasive such as sand, alumina, or granite chips and the drum rotated. Flashings, fins and oxide scale are removed by this process. Honing lapping and polishing These are abrasive finishing processes and only a small amount of metal removal occurs. Honing is a technique for sizing and finishing bored holes. The honing head carries four or six honing stones. These are made of abrasive particles bonded by a resin or wax. The honing head moves in the hole with a rot ting and a reciprocating motion, the stones being held against the work by a light pressure. 46. Non-traditional machining processes There is a range of material removal processes which do not involve the formation of chips. These non-traditional, or chipless, machining processes are suitable for use with a variety of materials, including very hard metals which, otherwise, would be difficult to machine, and some can be used in connection with ceramics. Chemical machining (CM) CM is the removal of material by controlled chemical attack. One form of chemical machining, engraving, has been in use for hundreds of years. The basic principle of chemical machining is to cover those parts which are not to be attacked by a mask or resist, so that only portions of the surface are etched away. Electrochemical machining (ECM) ECM is a metal removal process based on the solution of anode material in an electrolytic cell. The workpiece is made the anode and a tool, shaped so that it is a negative of the required component shape, is made the cathode of the cell. The tool is fed into the work at a constant rate, and equal to the rate of metal removal, thus maintaining a gap of about 0.01 mm between the tool face and the work. The electrolyte is not static, but is pumped around the system at high velocity, 30 m/s or greater. The high electrolyte flow rate is necessary as a major function of the electrolyte is to conduct heat away from the work. ECM is an expensive process but is of particular use in the machining of very hard complex alloys, such as the superalloys used for high temperature components in gas turbines. Electrodischarge machining (EDM) EDM, also referred to as spark erosion, is a machining process based on the erosive effect of an electric spark. Of the two electrodes used to produce a spark, one is the tool and one is the workpiece. The work is made positive because erosion of the positive electrode is greater than that of a negative electrode, other things being equal. The tool is produced to a shape which is a negative of the required machined component profile. The work and electrode tool are contained in a tank filled with a dielectric fluid, such as kerosene, white spirit, transformer oil or a glycerol/water mixture, and sparks at a high frequency are generated between tool and work. The gap between work and tool is kept at about 0.05 mm and the spark frequency may be between 400 Hz and 200 kHz, depending on the nature of the tool and workpiece, rate of metal removal and surface finish required. Electron beam machining (EBM) In this process, a high energy electron beam is focused onto the workpiece, which is contained in a vacuum chamber. The heat energy generated when the beam strikes the work is sufficient to melt and vaporise the material. EBM is used with extreme precision for making small diameter holes and slots in relatively thin materials. Holes with diameters as small as 2 μm can be made in very thin materials. The process may be used to drill holes in sapphire and other ceramics for use as bearings in delicate instruments. Laser beam machining (LBM) LBM is similar to EBM in that the intense heat generated when a finely focused laser beam strikes a material is sufficient to melt and vapourise the material. A laser beam can be focused down to a very small spot size, about 0.02 mm, and can be used for the drilling of very small holes in almost any metal in thicknesses of up to 2.5 mm. Unlike EBM, a laser beam does not have to be operated in vacuo. The energy of a laser beam can be used for the cutting of materials and almost any material can be cut. For the cutting of many metals, a jet of an inert gas or oxygen is directed at the area of cut to blow molten metal away. In the case of an oxygen jet, oxidation effects tend to accelerate the cutting process. Plasma jet machining A plasma is a highly ionised gas produced by heating a suitable gas, such as argon, to a very high temperature in a confined space. Plasmas can be created by passing the gas through a constricted electric arc. The plasma jet produced in a plasma arc torch can be used for metal cutting. The extremely high temperatures and jet action of the plasma will give relatively smooth cut surfaces. Very high cutting speeds are possible and cutting rates of 2.5 m/min have been achieved in steel plate of 12.5 mm thickness. et machining This is a slitting process suitable for cutting soft materials, including paper and paper products, some plastics, leather, rubber and GRP material, using a very high velocity fluid jet as the cutting medium. 47. Soldering and brazing of metals Soldering and brazing are techniques used for joining some metals and a material of a different composition from the metals to be joined is used to effect the joint. The solder or brazing alloy is of lower melting point than the metals to be joined and no portion of the parent metals is melted during the process. Soldering and brazing processes are similar in principle in that the filler material melts at a comparatively low temperature and this liquid filler is drawn by capillary action into the small gap between the parts being joined. One major advantage of soldering and brazing operations is that the joint is made at fairly low temperatures so that there is little heat distortion of parts and little change to the microstructure of the parent metal. Soft solders are comparatively weak but hard solders (brazes) may have tensile strengths in the range 400-500 MPa. Soft soldering Soft solders are alloys of tin and lead or tin/lead with antimony, cadmium or bismuth and have melting temperatures in the range 70-300°C. For soldering to be effective the liquid solder must 'wet' the surface of the metal to be soldered. This means that some alloying must take place between a constituent of the solder and the metal to be joined. The type of alloying that occurs may cause formation of a solid solution or the formation of an intermetallic compound. In soft solders tin will form intermetallic compounds with both copper and iron. A liquid solder will only wet a metal surface that is clean and grease free so all surfaces to be soldered must be perfectly clean. A thin oxide film will quickly form on a fresh metal surface and so a soldering flux is necessary to dissolve this oxide layer. The flux used is either zinc chloride solution or of the resin type. When the former flux is used the part must be washed after soldering to remove any remaining flux, otherwise corrosion could occur. When a resin flux is used any flux residue left after soldering is not corrosive. Soft solder wire with a resin core is invariably used for electrical jointing work. Hard soldering Hard soldering, or brazing makes use of copper-base alloys with melting temperatures ranging from 620°C to 900°C for making the joint. Again, the materials to be joined must be clean and a flux must be used. The most commonly used flux is borax. Borax melts at 750°C and is a good solvent for many metal oxides. For brazing at lower temperatures than this alkali metal fluorides are used as fluxes. As with soft soldering the parts to be joined are prepared and fitted together. During brazing the molten filler metal is drawn by capillary action into the joint. The most commonly used heat source for brazing is the oxy-gas torch. The gas used is propane or acetylene. Generally, a neutral or slightly reducing flame is used, but when brazing copper a slightly oxidising flame should be used to reduce the possibility of hydrogen embrittlemen. Furnace brazing Furnace brazing is a technique used for the mass production of small assemblies. The assemblies are made up and the filler placed in the joint, either as a powder or a preformed ring or disc. The parts are then placed in a controlled atmosphere furnace and heated to a temperature just above the melting temperature of the brazing filler. Hard solders Brasses, alloys of copper and zinc, are widely used as hard solders, hence the term brazing. The brasses used contain more than 40 per cent zinc but some zinc is lost during the operation and the final jointing metal possesses an α or (α + β) structure. The brazing alloys may contain small amounts of silicon or silver to increase the fluidity of the filler, or nickel and manganese to increase the strength of the joint. Braze welding This is a metal joining process in which the filler metal has a lower melting point than the metals to be joined but, unlike brazing, the molten filler is not drawn into the joint by capillary action. There is a wider gap between parts to be joined than in a brazed joint and the filler metal, typically either a brass or a bronze, is melted by means of an oxy-gas torch or an electric arc. When the filler material is a bronze the process is termed bronze welding. Aluminium solderingLead-tin alloys will not 'wet' an aluminium surface and it is not possible to solder aluminium using soft-solders. Aluminium can be soldered with these alloys using a chloride flux. This layer is put on during an early stage in manufacture by placing a cladding plate of aluminium-silicon alloy on the surface of an aluminium ingot and hot rolling them together. Fusion welding of metals As stated earlier, in fusion welding a filler material of similar composition to the metals being joined is generally used and during the process a portion of the metals being joined is also melted. There are very many fusion welding processes and the heat necessary for welding may be obtained from a chemical reaction or by using electrical power One of the first successful fusion welding processes to be developed was gas welding using heat energy from the combustion of acetylene in oxygen in a special torch. 48. Fusion welding of metals As stated earlier, in fusion welding a filler material of similar composition to the metals being joined is generally used and during the process a portion of the metals being joined is also melted. There are very many fusion welding processes and the heat necessary for welding may be obtained from a chemical reaction or by using electrical power. One of the first successful fusion welding processes to be developed was gas welding using heat energy from the combustion of acetylene in oxygen in a special torch. A fusion weld is a small casting and the actual weld area will tend to have the structure of a casting. During the welding process the temperature of the surrounding material will be raised and this may cause microstructural alterations in the area adjacent to the weld, the heat affected zone. 49. Gas welding The main type of gas welding is oxy-acetylene, in which acetylene (ethine) and oxygen are mixed and burnt in a torch. The full and complete combustion of acetylene is 2C2H2 + 5O2 = 4CO2 + 2H2O (53.4 MJ/m3 acetylene) In this reaction the ratio oxygen volume/acetylene volume is 5/2. In practice the volume ratios of oxygen/acetylene entering the torch are much less than this and normally range from 0.85/1 to 1.7/1. For a ratio of 1/1 the reaction equation would be C2H2 + O2 = 2CO + H2 (18.3 MJ/m3 acetylene) The carbon monoxide and hydrogen reaction products of this equation then burn with atmospheric oxygen at the outer envelope of the flame. By controlling the relative amounts of oxygen and acetylene, flames with differing characteristics can e obtained. A chemically neutral flame is obtained when the oxygen/acetylene ratio is about 1.1/1, with a flame temperature of about 3250°C. If the oxygen/gas ratio is increased a shorter, fiercer, oxidising flame with a temperature of about 3500°C is produced, while an oxygen/gas ratio of about 0.9/1 will give a chemically reducing flame with a flame temperature of about 3150°C Gas welding is less widely used than the electric arc processes but it is still an important process. The gas torch can be used to pre-heat the joint area and to reduce the rate of cooling after welding. This is a great advantage when welding hardenable steels, as it reduces the possibility of brittle martensite formation in the weld zone. 50. Pressure welding of metals The oldest form of pressure welding is forge welding in which two pieces of wrought iron are heated to red heat and hammered together to make a weld. The slag within the wrought iron acts as a flux. Similarly, mild steel can be forge welded with a little silica sand used as a flux. Most of the pressure welding processes used industrially today are of the electric resistance type. The range of pressure welding processes is shown in Figure 51. The welding of plastics. Welded joints can be made in most thermoplastics and many can be joined using adhesives. Fully cured thermosets cannot be welded and any joints required are made using eiyher adhesives or mechanical fastenings. Hot gas welding is a fusion welding process for thermoplastics which resembles the oxy – gas welding of metals but the heat source is a jet of heated gas rather than a flame. Air or an inert gas is passed through a torch, where it is heated by either gas or electrical heating, and used to melt the joint surfaces and the thermoplastics. Hot plate welding. The parts to be joined are heated by an electrically heated resistance strip or a heated metal plate, the softened areas brought together and cooled under pressure. In some cases, a strip or rod of the thermoplastic can be used as a filter material in order to improve the joint quality. Spin welding is reserved for the joining of metal parts and the welding of thermoplastics is referred to as spin welding. It is a welding technique whereby the frictional heat generated by the rapid rotation of one thermoplastic component against a second, stationary thermoplastic part causes localised surface melting of both parts. Vibration welding. The frictional heat generated at the mating surfaces of thermoplastic parts when one of the parts is subject to a low – frequency oscillation is sufficient to cause localised melting and the two parts fuse together. Thermoplastics are dielectrics and dielectric heating occurs when they are placed in a high frequency electromagnetic field. The principle of electromagnetic induction heating can be used for the welding of thermoplastics. Some thermoplastics can be softened and joined with the aid of specific solvents. 52. Forming of thermoplastics. The majority of thermoplastic materials posses comparatively low softening and melting temperatures and the termed melt processale. Casting. Some thermoplastic materials may be cast into shape in moulds and allowed to solidify. Casting is not a widely used process for thermoplastics but it used for some polyamide and acetal products. It is also suitable as a production process when only a limited number of items of any particular design is required and the small number does not justify the high cost of makinga set of dies for injection moulding. 53. Forming of thermosets. The thermosetting plastics are produced by condensation polymerisation and the reaction must be stopped before completion, as the raw plastic for moudling is required in a part – polymerised condition. The polymerisation is completed during the moulding process to give a full network rigid structure. The raw plastic material is normally compounded with fillers in order to produce a moulding compound. The principal forming processes for thermosetting plastics are compression moulding and transfer moulding. In compression moulding, the moulding power is compressed between the two parts of a heated metal mould, or die. The power becomes plastic and flows into the recesses of the mould. The pressure is maintained until the polymer has cured, that is, until full polymerisation has occurred and the material has set rigid. Compression moulding is not suitable for the moulding of shapes of thick section, or with large changes of section. The cold setting rigid plastics may be readily into shape by casting. 54. Ceramics and cermets. Gradually this meaning was extended to include all products made from fired clay, such as bricks, tiles, fireclay refractories, and electrical porcelain, as well as pottery tableware. Many substances now classed as ceramics in fact conmtain no clay, though all are relative hard, brittle materials of mineral origin, with high fusion temperatures. Thus materials like glass, vitreous enamel, and hydraulic cement are now included under the general heading of ceramics; whilst a number of metallic oxides such as alumina, beryllia, zirconia, and magnesia from the basis of high – temperature ceramics. High – temperature ceramics. Gas – turbine and turbo – jet blades made from ceramic materials can be used at higher temperatures than those made from the most refractory metallic alloys. Cermets generally are suitable for such uses as lamp filaments; aircraft jet – engine parts; gas – turbine parts; rocket – engine components; cutting-, drilling-, and grinding – tools; friction parts; nuclear – power applications; heating – elements; bearings; and magnetic – core materials. 55. Forming of clay ceramics. Clay materials are normally shaped from a moist soft plastic mass. Hand throwing in the age old manner is still used on a small scale, but for mass production the process is automated and the potter’s hands have been replaced by moulds and templates. After shaping, clay articles are dried and then fired in a kiln at temperatures in the range 800 – 1500°C. The firing causes expulsion of water of crystallisation, and a recrystallisation, creating a rigid, through brittle material. Another method used clay shapes in slip casting. The slip, which is a thick slurry or suspension of clay in water is poured into a porous mould. Water is rapidly absorbed into the mould from the slip, and the surface layers of the slip become solid. Another method is tape casting. This method is used to produce thin ceramic wafers for use in the electronics industry. The slip is filtered and fed onto a continuous moving belt, the thickness of the deposited film being controlled by an adjustable gate. 56. Sintering. Sintering is a term for the process which converts a powder compact into a solid polycrystalline material. It is a thermally activated process and the driving force is the reduction in surface energy which occurs as the powder particles coalesce. In solid phase sintering, which is carried out at temperatures below the melting points of the powderconstituents, the first stage in the process is the transport of some material by diffusion and its deposition in the inter – particle spaces immediately adjacent to particle contact points. This deposit is termed a neck, and the formation of necks increases the particle contact area. During sintering, the necks grow and merge with one another until, eventually, the original particle structure is replaced by a polycrystalline grain structure with a network of porosity between grains. Sintering under pressure will produce higher density materials with finer grain sizes than is possible with sintering at atmospheric pressure. The two forms of pressure sintering are hot – pressing, where the compact is sintered under pressure in a heated graphite or ceramic die, and hot isostatic pressing, in which a preformed compact is sintered at high temperature. Another form of sintering which may be used to produce dense ceramics with little or no porosity is liquid phase sintering. 57. Manufacture of glass. The raw materials for the manufacture of common soda – lime – silica glass are soda ash. These ingredients are crushed and ground to a fine particle size. During melting, the carbonates decompose, libreting carbon dioxide, and react with the silica. The gas evolution agitates the melt and aids themixing to achieve a uniform composition. Glass tanks are divided into two zones, the melting and refining zone, and the working area, a bridge wall separating in two areas.
Šį darbą sudaro 13789 žodžiai, tikrai rasi tai, ko ieškai!
★ Klientai rekomenduoja
Šį rašto darbą rekomenduoja mūsų klientai. Ką tai reiškia?
Mūsų svetainėje pateikiama dešimtys tūkstančių skirtingų rašto darbų, kuriuos įkėlė daugybė moksleivių ir studentų su skirtingais gabumais. Būtent šis rašto darbas yra patikrintas specialistų ir rekomenduojamas kitų klientų, kurie po atsisiuntimo įvertino šį mokslo darbą teigiamai. Todėl galite būti tikri, kad šis pasirinkimas geriausias!
Norint atsisiųsti šį darbą spausk ☞ Peržiūrėti darbą mygtuką!
- Medžiagotyros konspektas
- 5 psl., (13789 ž.)
- Word failas 131 KB
- Lygis: Universitetinis
Mūsų mokslo darbų bazėje yra daugybė įvairių mokslo darbų, todėl tikrai atrasi sau tinkamą!
Panašūs darbai
Kiti darbai
Privalumai
Atsisiuntei rašto darbą ir neradai jame reikalingos informacijos? Pakeisime jį kitu nemokamai.
Pirkdamas daugiau nei vieną darbą, nuo sekančių darbų gausi 25% nuolaidą.
Išsirink norimus rašto darbus ir gauk juos akimirksniu po sėkmingo apmokėjimo!
Atsiliepimai